Topic overview
What is an Antenna and What is it Used For?
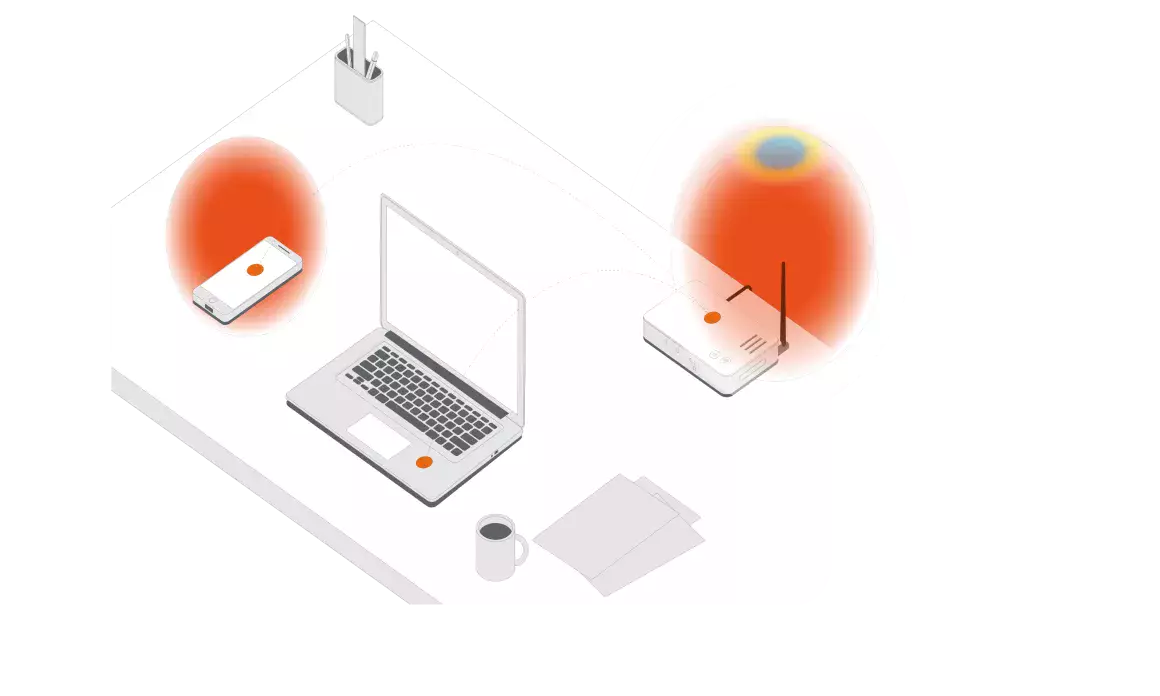
An antenna is a crucial component in modern communication systems. Its role, the transmission and reception of electromagnetic energy, is the key to all means of wireless transfers of data, communications and more. The transformed energy can come in various forms: radio waves, cell phone signals, and radar signals.
Antennas are designed for specific applications. There are different types of antennas and they can be very small or extremely large, and their designs can vary widely from simple to complex.
This introductory article goes back to the basics of the device itself and its useful purpose.
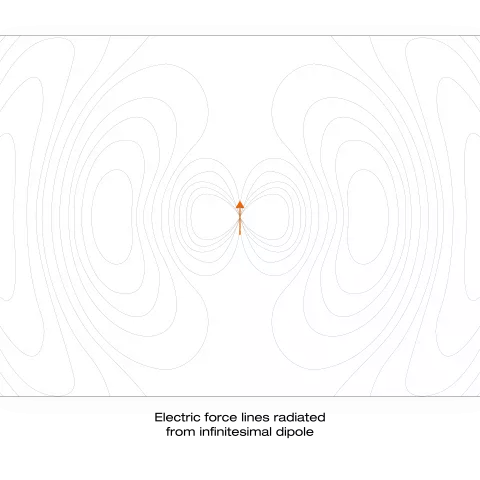

How Do Electromagnetic Fields Relate to Antenna Operation?
Antennas are used to transmit and receive electromagnetic energy. To understand how this energy propagates through space, a few principals of electromagnetic waves and how they function is required. EM fields change as a function of both distance & time.
In this 2nd article, we will examine the case of a simple dipole antenna radiating at a single frequency to explain electromagnetic fields and their relation to antennas.
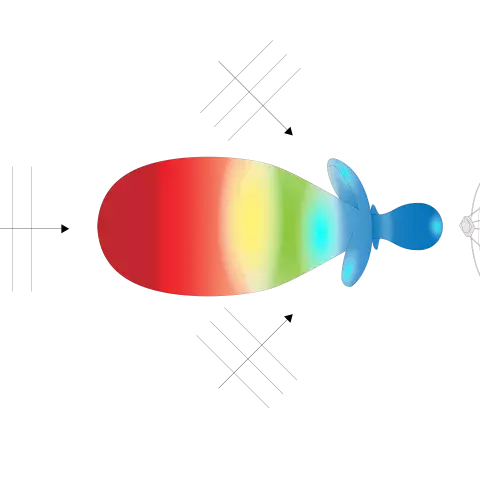
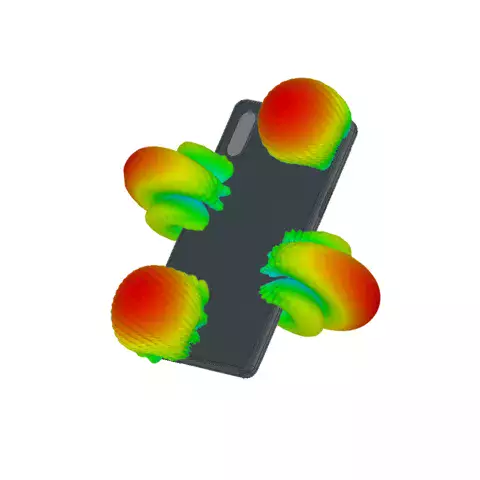
How Can we Accurately Measure an Antenna's Response?
As antennas are designed to operate at a certain distance from one another, for a measurement, we need to determine the area between them where the electromagnetic waves are flat, in other words, where they become plane waves. This is known as the far field. Ideally, we would like to measure an antenna’s response to a plane wave in any direction.
This 3rd article will delve into the importance of the electromagnetic fields, time and distances between signals, and the interferences to be avoided in order to perform accurate measurements.
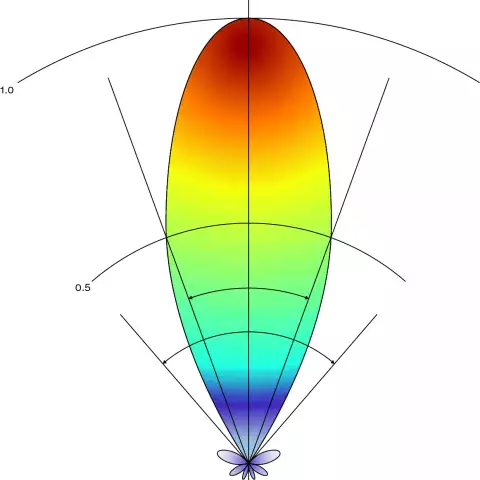
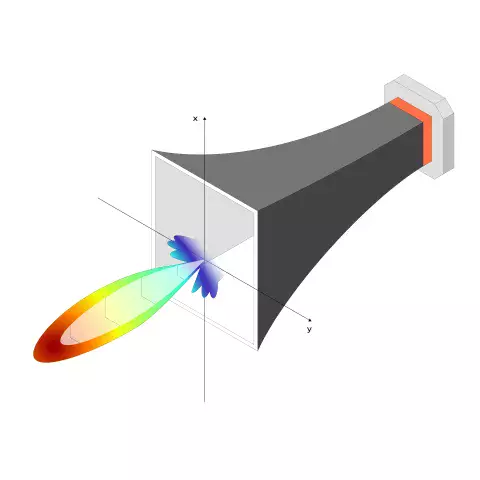
What is the Anatomy of Radiation and Power Patterns?
An antenna radiation pattern is a graphical representation that describes how an antennna radiates or receives electromagnetic waves in three dimensions. It illustrates the strength and directionality of the radiated or received electromagnetic energy as a function of the angle. The radiation pattern is typically visualized using a polar plot, which shows the power or field strength of the radiated waves at different angles around the antenna, but can be viewed in a variety of ways for clarity in analysis.
Radiation patterns just like directivity, polarization impedance, gain, or efficiency are a metric for measuring the antenna performance.
In this 4th article, we explore the anatomy of an antenna radiation pattern, its purpose and role in antenna measurements.